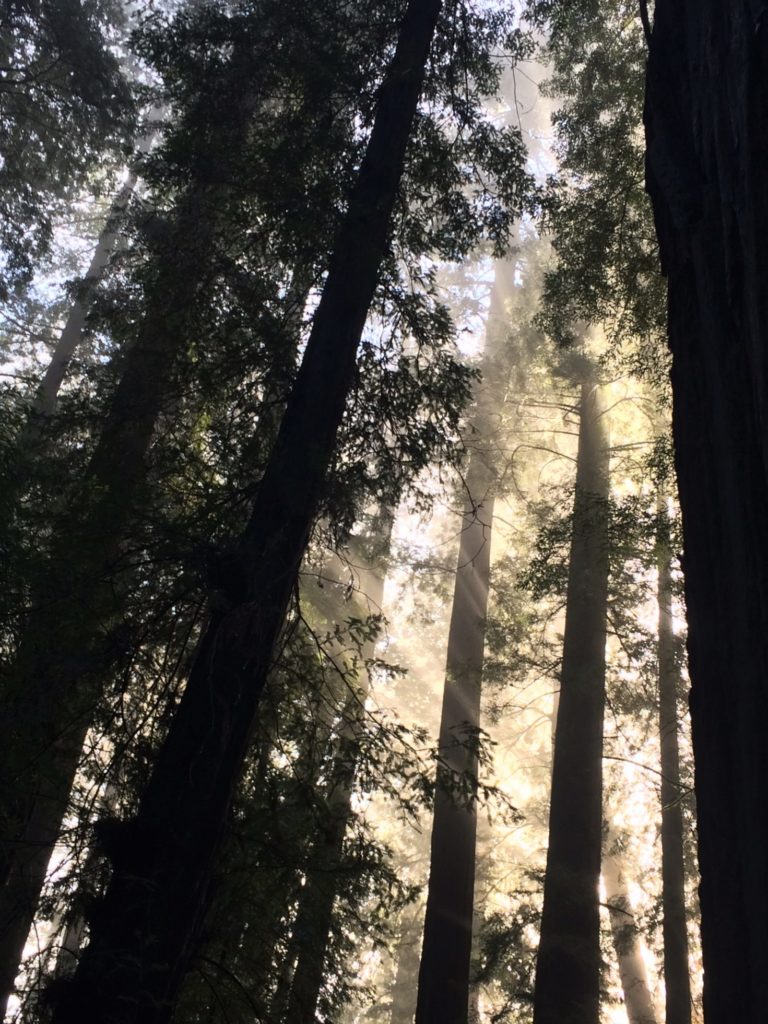
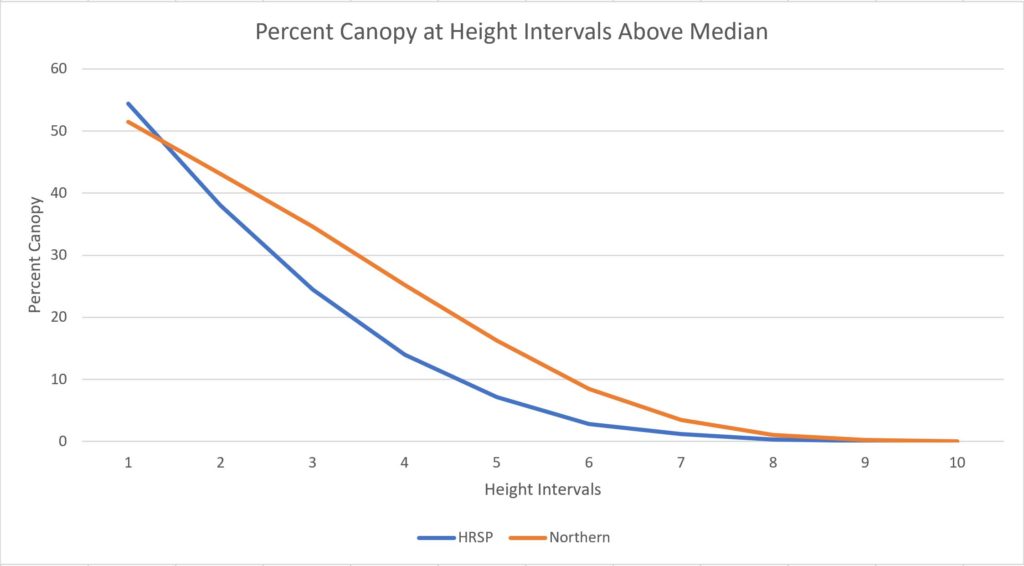
A couple months ago (mid September 2023) I took a few days to visit the redwood parks and forests in Santa Cruz, Mendocino, and Humboldt counties in California. I also caught up with a few redwood colleagues, it was nice visiting and doing some walking and hiking.
Day One – Big Hendy and Little Hendy Groves in Hendy Redwoods State Park near Philo
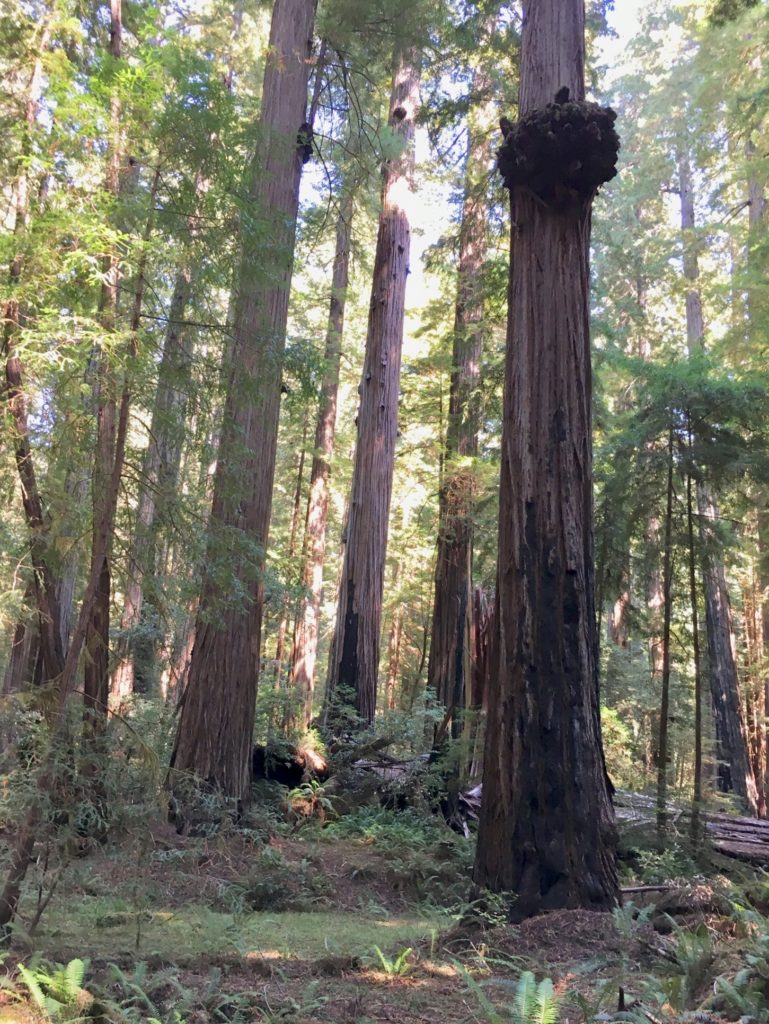
Big Hendy redwood grove has well maintained relatively flat trails that wind throughout the old growth area. There are tall trees here, with twenty or so from 330-350 feet in height. There is also a nice prairie area adjacent to the river and good picnic facilities.
Little Hendy redwood grove is a smaller though just as nice grove closer to the visitor center and is pretty much right above the banks of the Navarro River. The primary trail is a single narrow oval loop with small elevation changes. There are some large and unusual redwoods in Little Hendy Grove right along the loop.
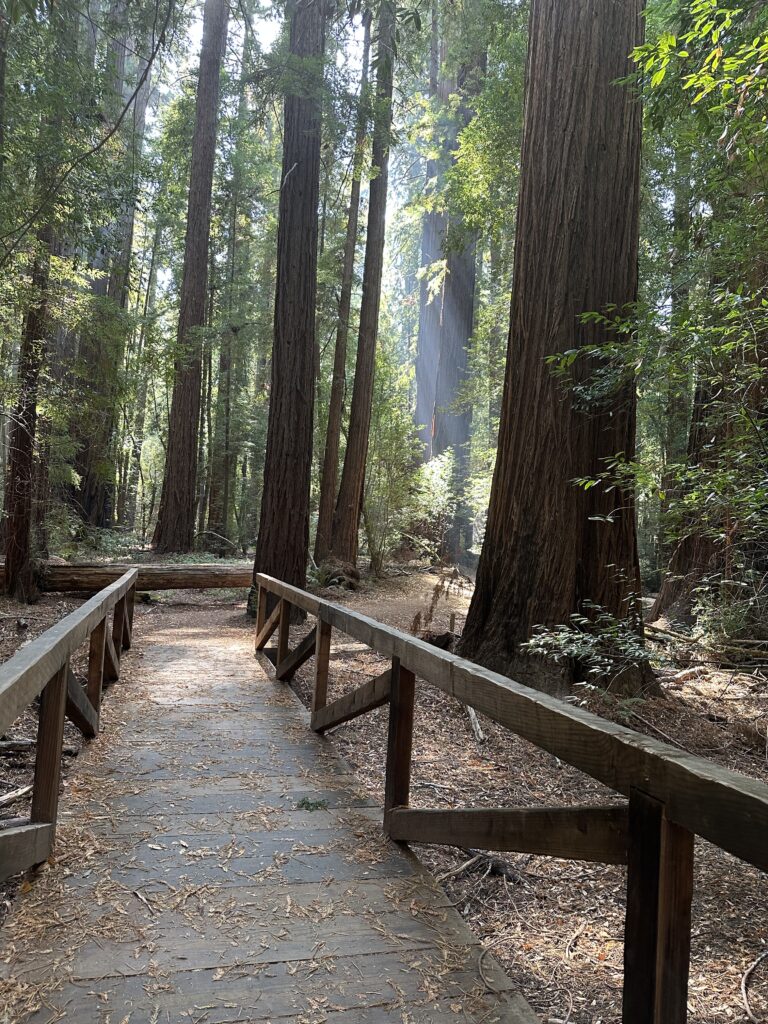




Day Two – Humboldt Redwoods State Park Bull Creek Groves
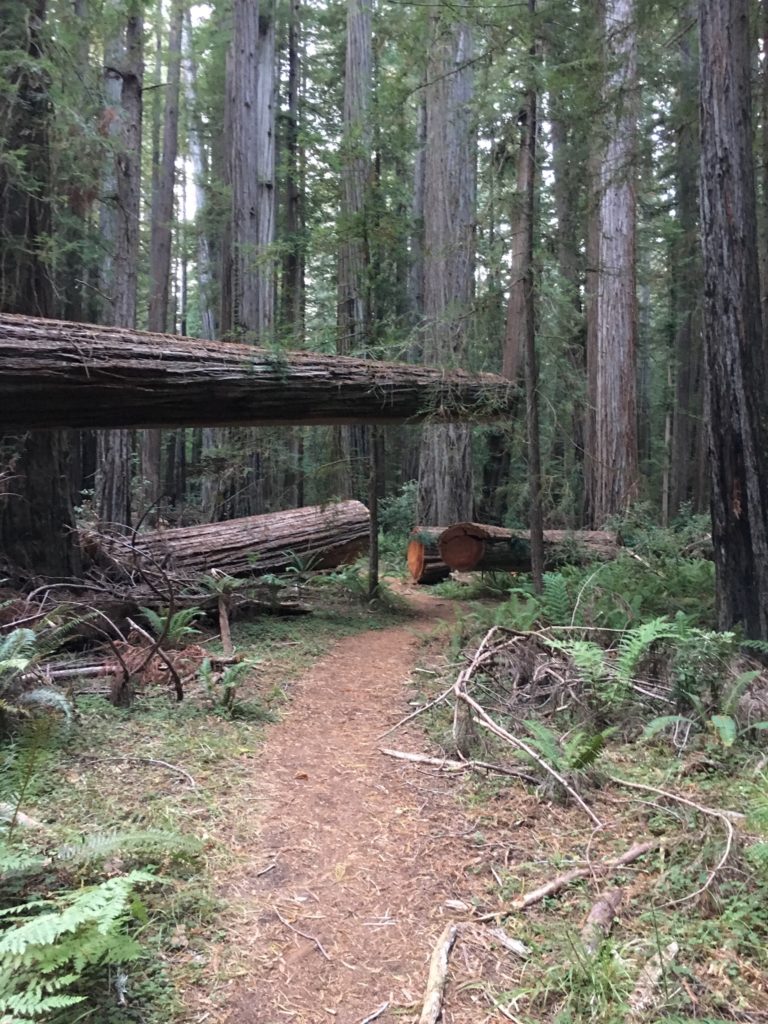
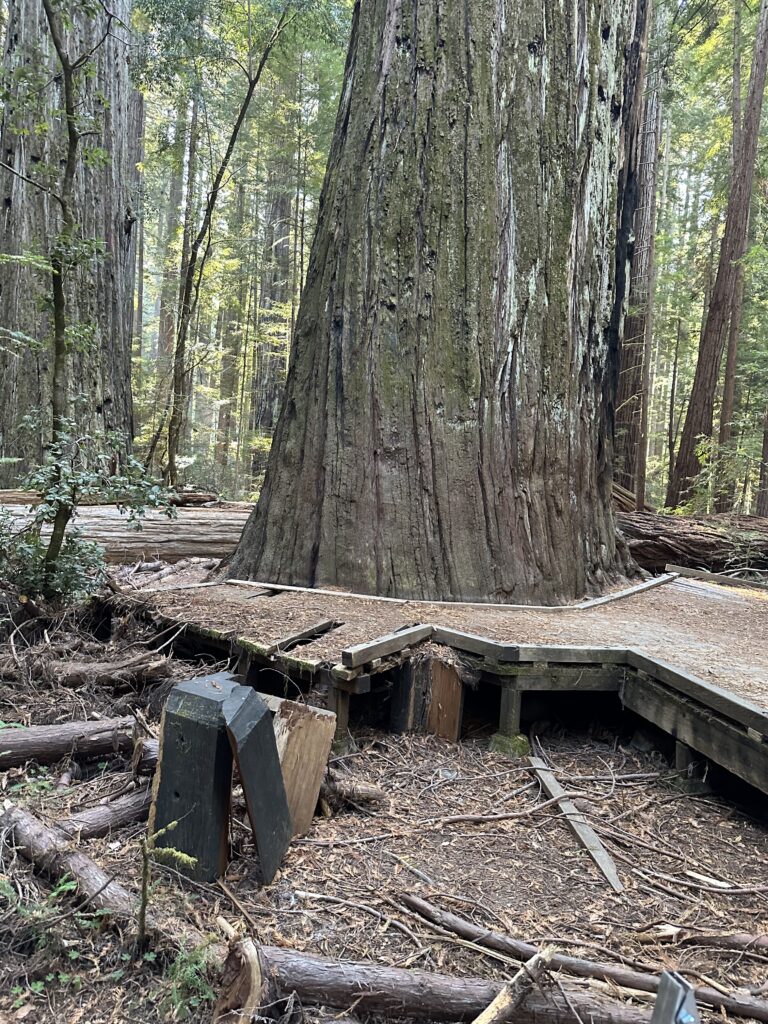
I met John (the Eagles fan John) in the Tall – Giant tree area off Mattole Road. We did some hiking in the flats on both sides of Bull Creek. There were a few downed trees, especially on the north side of Bull Creek. The Giant Tree dropped a big limb or two recently, smashing through the deck surrounding it and destroying the sign beside the deck. There is also a big deep hole in the ground on the west side of the Giant Tree, obviously involving the Giant Tree’s roots. It is worrisome.
The drive along Mattole Road took me though the area where there was a big landslide last Spring. About a quarter mile of the road is now gravel track, and there are many downed redwoods on the downhill side of Mattole Road through this area.



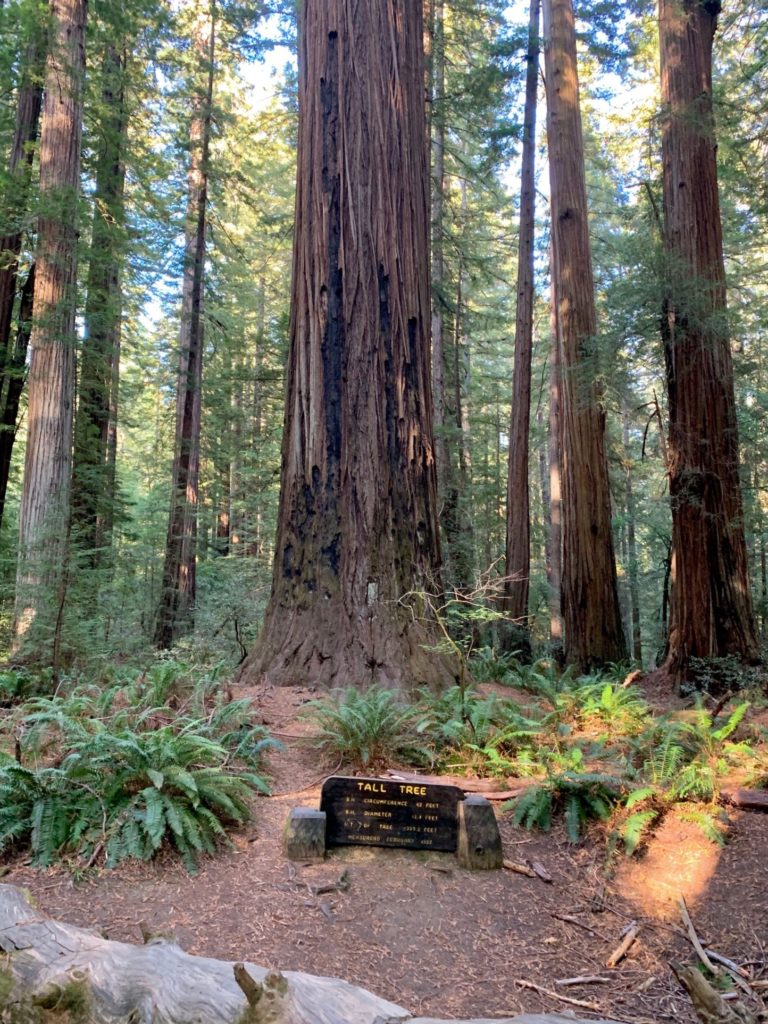
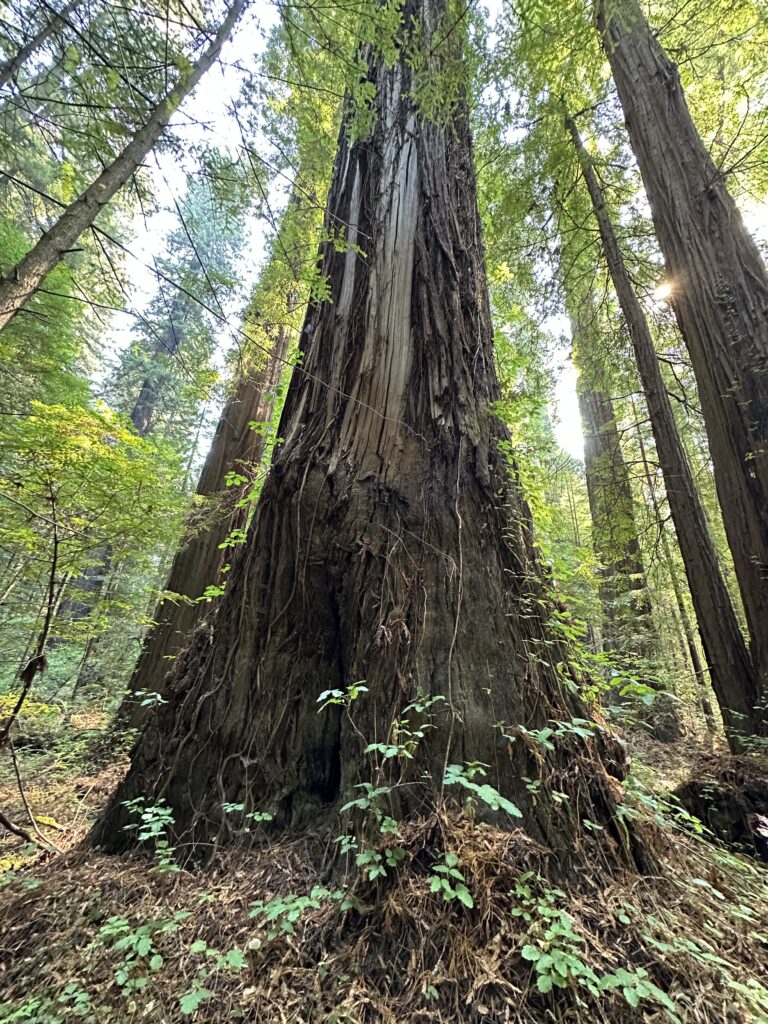
Day Three – Redwoods National Park Tall Trees Grove
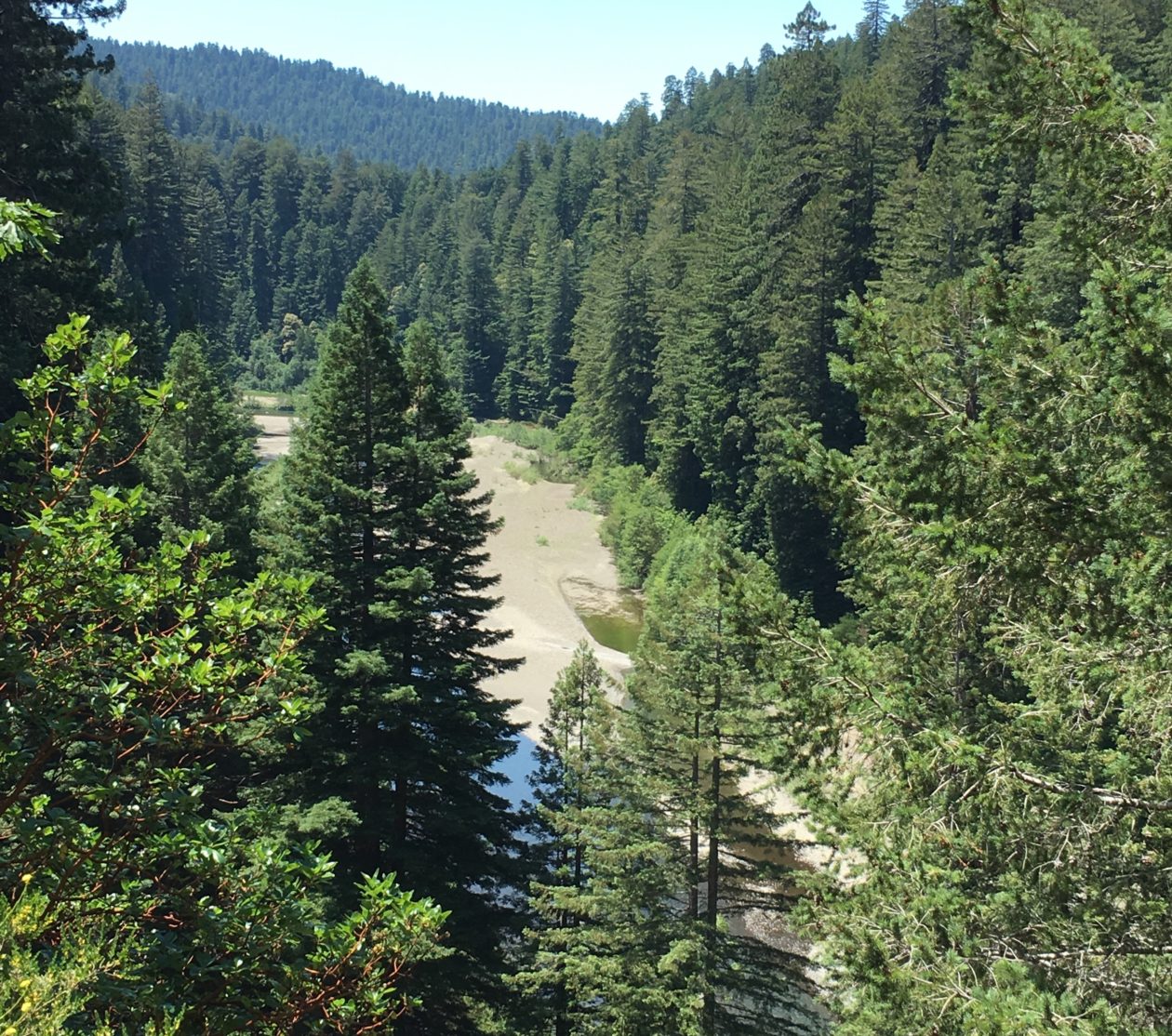
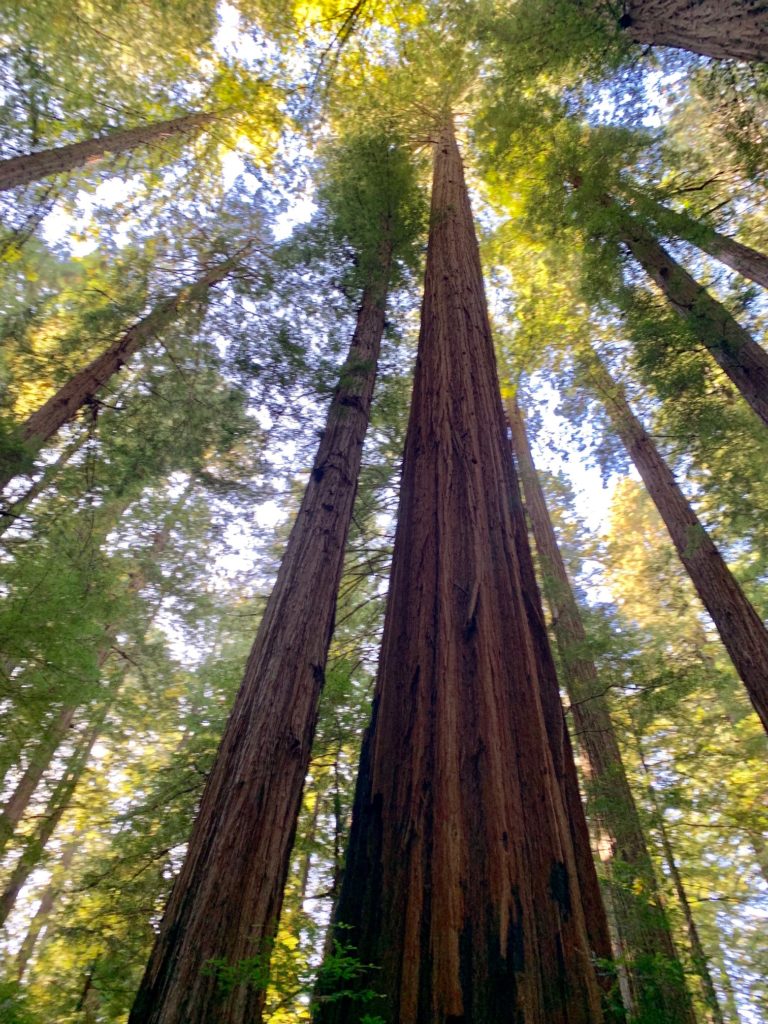
I really enjoy the drive and hike to Tall Trees Grove, and the grove itself is great. In the summer walking out onto the gravel bars of Redwood Creek from the Tall Trees trail is a must to see the giants in profile. These redwoods are huge living things.
There was a lot of tree fall along upper Tall Trees grove trail last winter and many well executed repairs are visible on the upper part of the trail. Down in the grove itself all the giants seem to be standing tall. I spent a lot of time on the gravel bars taking in the views, both immediate and long distant. The hike back up the steep hill is a good leg and lung stretcher and I enjoyed respites on a couple of well positioned benches.





Day Four – Humboldt Redwoods Pepperwood Area, Smithe River State Natural Reserve, and Chamberlain Creek Waterfall Trail in Jackson State Forest Mendocino County
On day four I met Steve (the Cal Poly Humboldt Steve) and we did some hiking and work in the Pepperwood Area of Humboldt Redwoods State Park. Most of the time we were in French Bell Grove, but we also went over to the north end of the Avenue to check out a few trees close to 101.
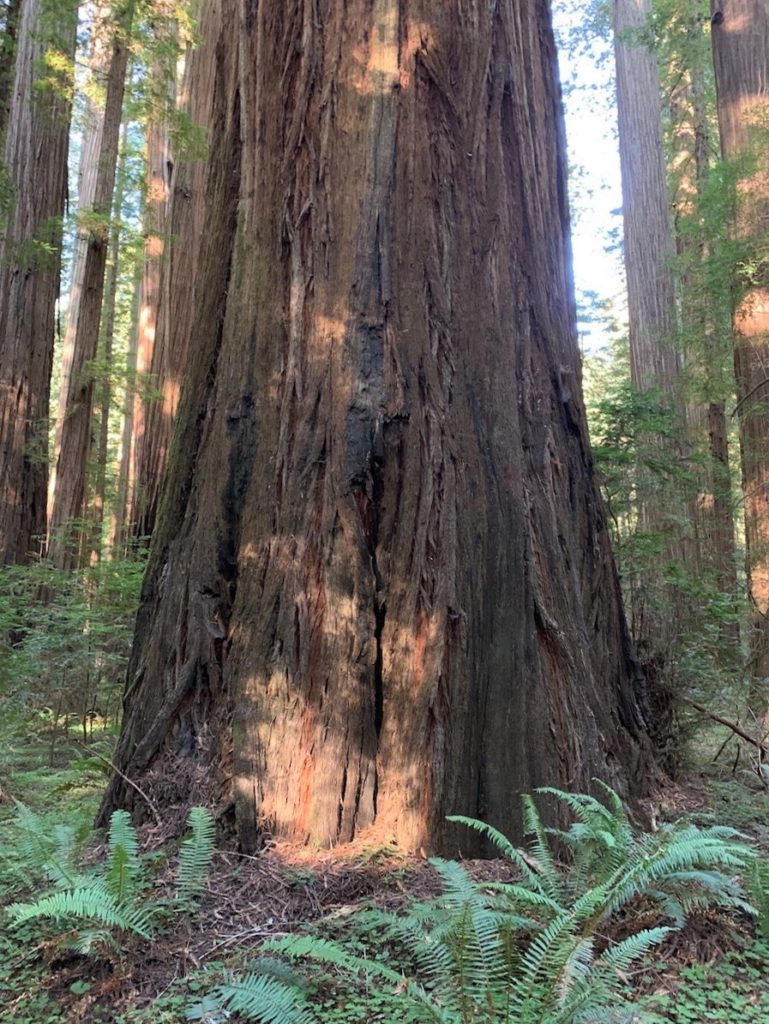
Later that day I finally stopped at Smithe Redwoods State Natural Reserve along 101 north of Leggett. Care needs to be taken exiting and entering 101 from the adjacent parking area as this is a high-speed curvy area of the highway. Smithe Redwoods are on a nice flat above the Eel River and there is some impressive old growth there. A couple trees top out at 330 feet.
After this it was off to Chamberlain Creek Waterfall Trail between Willits and Fort Bragg in Jackson State Demonstration Forest in Mendocino County. This area is a little remote and has gravel roads on the approach and it is good to have well researched written directions when driving there. The trail is great, it starts from a road and moves sharply downhill into a creek valley filled with tall old growth redwoods. The waterfall was flowing, and the wide cascade drops straight down a twelve foot or so wall of rock. The waterfall and redwoods are in the same immediate area, so the vista is scenic and tranquil.






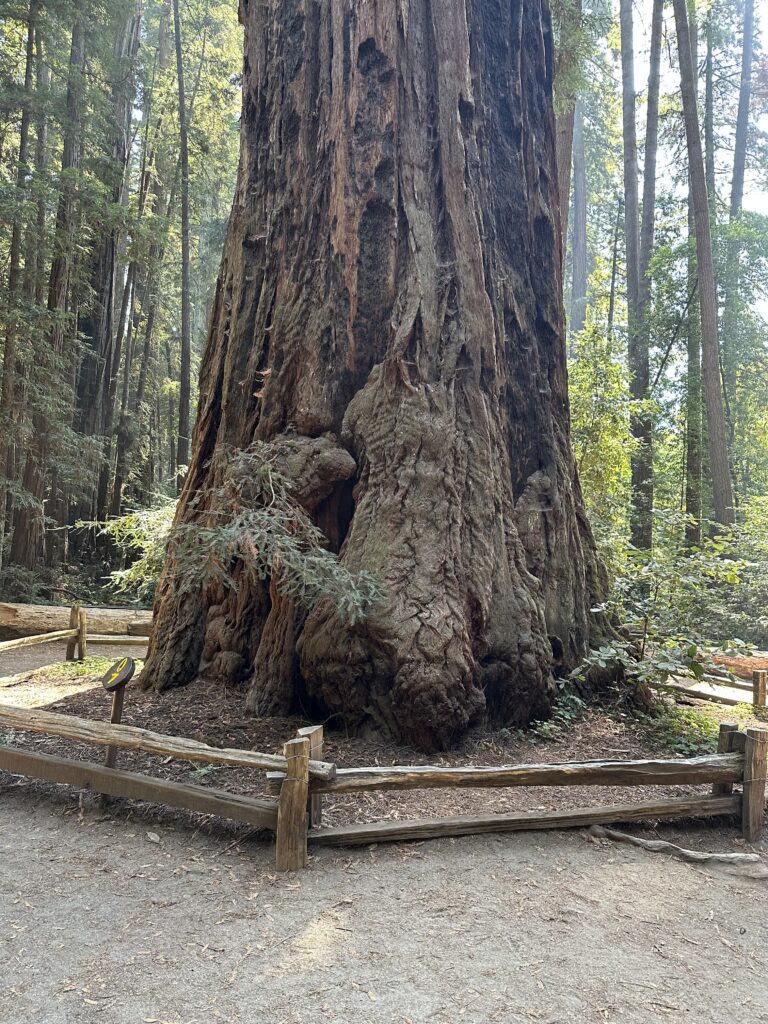
Day Five – Henry Cowell Redwoods State Park and Aptos Creek in Santa Cruz County
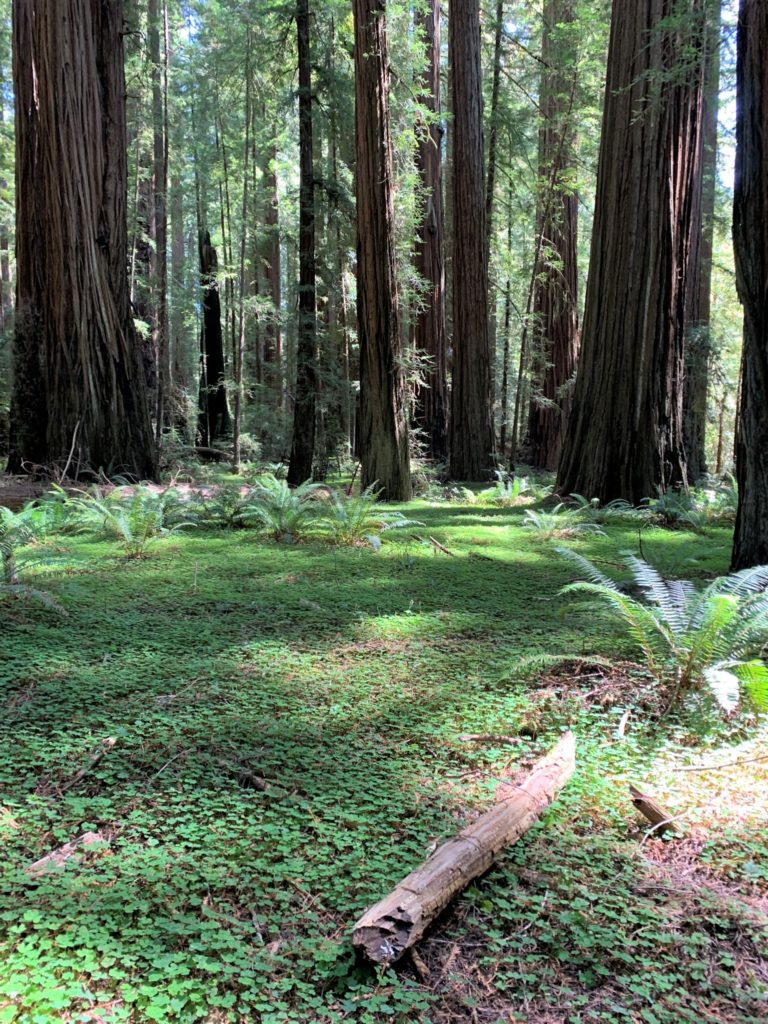
The drive on day five was very interesting, taking expressways through the South Bay area and then the winding roads to the Felton – Henry Cowell Redwoods State Park – Roaring Camp area. Henry Cowell Redwoods are beautiful, on a flat right above the San Lorenzo River. There are many really big redwoods along the primary old growth trail. This park has really nice facilities and a big parking lot near the trail entrance to handle a good number of visitors.
Later that afternoon I drove over to the Aptos Creek area to visit Ed (the Redwood Ed) and we took a nice walk and saw some big redwoods along Aptos Creek, very close to the Pacific Ocean.



I enjoyed my time in the redwood areas and meeting up with some good people. Thanks for reading.